Chronic Knee Pain
If you experience chronic knee pain, rather than inflammation or irritation after exercise or long periods of excessive activity or inactivity, you should contact a physiotherapist. They will be able to recommend a specific knee pain support treatment plan that suits you.
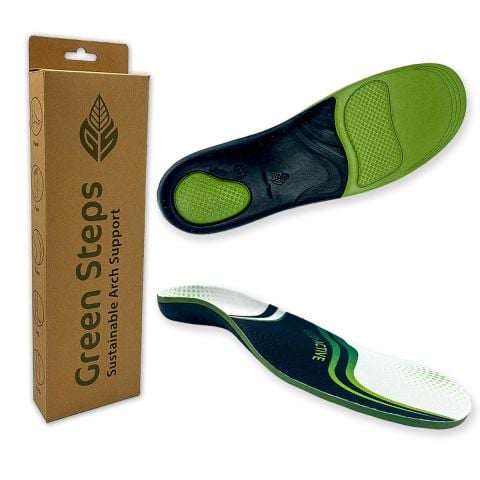
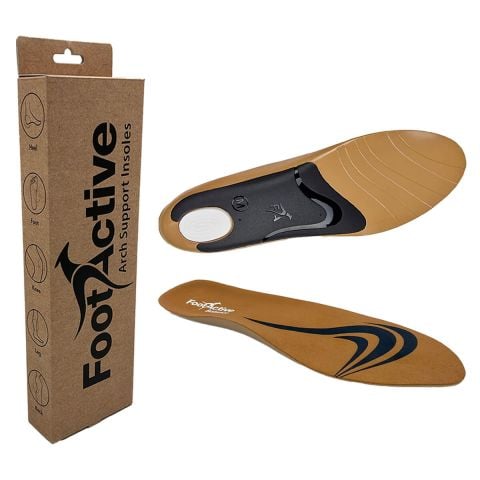
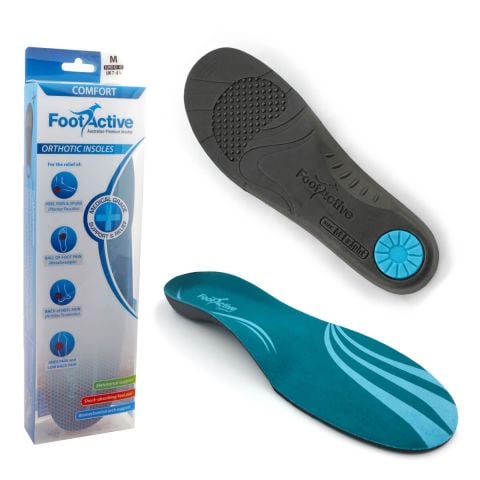
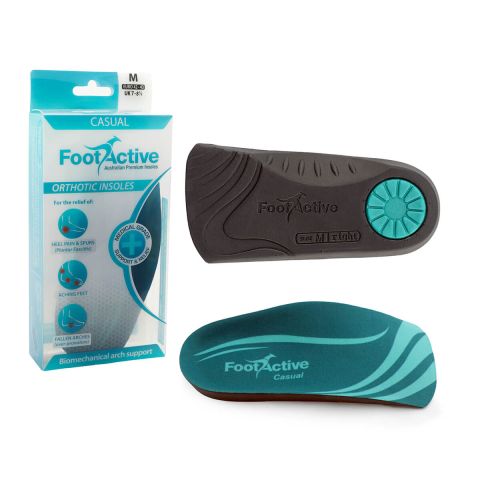
For more information regarding at-home advice and our full range of everyday and sports insoles for the best knee pain relief, contact FootActive today!
What Causes Knee Pain?
Knee pain is amongst the most common complaints in the UK, affecting a wide variety of people at all stages of life. In children, the cause is often growth pains such as Osgood-Schlatter disease which can last throughout adolescence and teenage years, caused by rapid growth that puts stress on the knee. In adulthood, chronic knee pain is commonly caused by exercise and stress injuries. It is natural to experience more frequent injuries as time goes on, as stress fractures and strains occur over time due to impactful activities. As a result, it is important to protect the knee with appropriate supports and correct positioning. To reduce the risk of worsening an injury, knee pain support and treatment should be an ongoing effort, rather than simple pain relief.
There are various causes of knee pain and it can be due to a combination of factors. What causes knee pain is often the wear and tear that occurs with age and general usage. Softening of the cartilage beneath the kneecap (patella) results in small areas of breakdown and pain around the knee. Instead of gliding smoothly over the knee, the kneecap rubs against the thigh bone (femur) when the knee moves. These changes can range from mild to complete erosion of the cartilage, causing extreme pain.
Another very common cause of chronic knee pain is fallen arches in the feet. What causes knee pain here is when the knee forms the link between the upper and lower leg and is a hinge joint designed to flex and extend the lower leg, not to rotate it. When the foot rolls inwards, the lower leg is forced to rotate, inevitably leading to wear and tear of the knee joint, causing long-term damage and pain.
Of course, one-off injuries can also be what causes knee pain, but you are more likely to experience the following if you already suffer from long-term chronic knee pain:
- ACL Injury (ligament tear)
- Fractures
- Torn Muscles
- Patellar Tendinitis
How To Reduce Knee Pain
Knee pain treatment for stress or long-time concerns is preventative rather than reactive. When considering how to reduce knee pain, general health, combined with the use of orthopaedic inserts, is an important combination for the success of any knee pain support plan.
Factors that can impact your knees, include:
- Your Weight – Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce the mass and impact on your knees and act a sone of the best knee pain relief methods.
- Full Body Workouts – What causes knee pain is often stress from other areas of the body, particularly the feet, but also the back, quads and calves. Exercises that condition and strengthen these areas are an excellent option in how to reduce knee pain.
- High Impact Sports – If you do suffer from the complaint, the best knee pain relief method is to avoid high-impact sports such as anything that involves jumping as this is what causes knee pain very often.
FootActive orthopaedic insoles are one of the best knee pain relief options and can prevent over-pronation, helping you restore proper knee function. As a result, what causes knee pain most frequently is comforted, thereby reducing, or eliminating knee pain and acting as one of the best knee pain relief methods.
Simple at-home pain relief can be used to compliment preventative knee pain support treatments, including ice and heat rotations. If you experience chronic knee pain it is imperative you do not depend on over-the-counter pain medication. Natural alternatives are actually more effective anti-inflammatories than some pain relief medications and are the best chronic knee pain relief option. First Honey can reduce heat and inflammation in the aggravated area.